Set up the dbt Semantic Layer
With the dbt Semantic Layer, you can centrally define business metrics, reduce code duplication and inconsistency, create self-service in downstream tools, and more.
Prerequisites
- Have a dbt Cloud Team or Enterprise account. Single-tenant accounts should contact their account representative for setup.
- Ensure your production and development environments use dbt version 1.6 or higher.
- Use Snowflake, BigQuery, Databricks, or Redshift.
- Create a successful run in the environment where you configure the Semantic Layer.
- Note: Semantic Layer supports querying in Deployment environments; development querying is coming soon.
- Understand MetricFlow's key concepts powering the dbt Semantic Layer.
- Note that the dbt Semantic Layer doesn't support SSH tunneling for Postgres or Redshift connections. It also doesn't support using Single sign-on (SSO) for production credentials, though SSO is supported for development user accounts.
📹 Learn about the dbt Semantic Layer with on-demand video courses!
Explore our dbt Semantic Layer on-demand course to learn how to define and query metrics in your dbt project.
Additionally, dive into mini-courses for querying the dbt Semantic Layer in your favorite tools: Tableau, Excel, Hex, and Mode.
Set up dbt Semantic Layer
You must be part of the Owner group and have the correct license and permissions to set up the Semantic Layer at the environment and project level.
- Enterprise plan:
- Developer license with Account Admin permissions, or
- Owner with a Developer license, assigned Project Creator, Database Admin, or Admin permissions.
- Team plan: Owner with a Developer license.
- Free trial: You are on a free trial of the Team plan as an Owner, which means you have access to the dbt Semantic Layer.
1. Select environment
Select the environment where you want to enable the Semantic Layer:
- Navigate to Account settings in the navigation menu.
- On the Settings left sidebar, select the specific project you want to enable the Semantic Layer for.
- In the Project details page, navigate to the Semantic Layer section. Select Configure Semantic Layer.
- In the Set Up Semantic Layer Configuration page, select the deployment environment you want for the Semantic Layer and click Save. This provides administrators with the flexibility to choose the environment where the Semantic Layer will be enabled.
2. Add a credential and create service tokens
The dbt Semantic Layer uses service tokens for authentication which are tied to an underlying data platform credential that you configure. The credential configured is used to execute queries that the Semantic Layer issues against your data platform.
This credential controls the physical access to underlying data accessed by the Semantic Layer, and all access policies set in the data platform for this credential will be respected.
| Feature | Team plan | Enterprise plan |
|---|---|---|
| Service tokens | Can create multiple service tokens linked to one credential. | Can use multiple credentials and link multiple service tokens to each credential. Note that you cannot link a single service token to more than one credential. |
| Credentials per project | One credential per project. | Can add multiple credentials per project. |
| Link multiple service tokens to a single credential | ✅ | ✅ |
If you're on a Team plan and need to add more credentials, consider upgrading to our Enterprise plan. Enterprise users can refer to Add more credentials for detailed steps on adding multiple credentials.
1. Select deployment environment
- After selecting the deployment environment, you should see the Credentials & service tokens page.
- Click the Add Semantic Layer credential button.
2. Configure credential
- In the 1. Add credentials section, enter the credentials specific to your data platform that you want the Semantic Layer to use.
- Use credentials with minimal privileges. The Semantic Layer requires read access to the schema(s) containing the dbt models used in your semantic models for downstream applications
-
Use Extended Attributes and Environment Variables when connecting to the Semantic Layer. If you set a value directly in the Semantic Layer Credentials, it will have a higher priority than Extended Attributes. When using environment variables, the default value for the environment will be used.
For example, set the warehouse by using
{{env_var('DBT_WAREHOUSE')}}in your Semantic Layer credentials.Similarly, if you set the account value using
{{env_var('DBT_ACCOUNT')}}in Extended Attributes, dbt will check both the Extended Attributes and the environment variable.
3. Create or link service tokens
- If you have permission to create service tokens, you’ll see the Map new service token option after adding the credential. Name the token, set permissions to 'Semantic Layer Only' and 'Metadata Only', and click Save.
- Once the token is generated, you won't be able to view this token again so make sure to record it somewhere safe.
- If you don’t have access to create service tokens, you’ll see a message prompting you to contact your admin to create one for you. Admins can create and link tokens as needed.
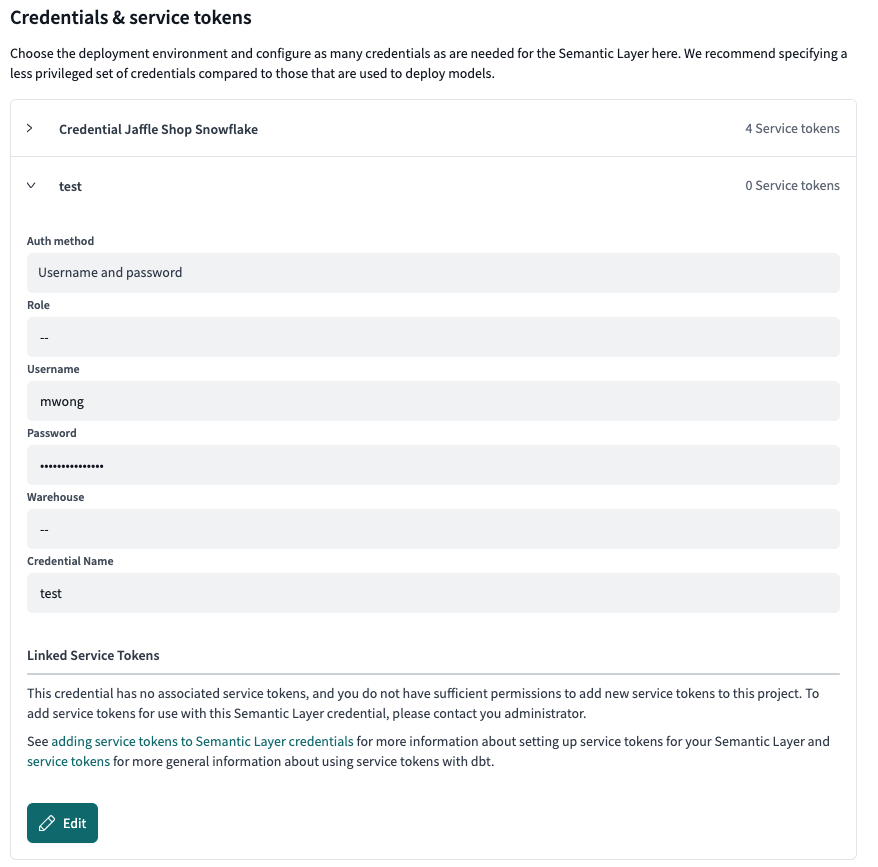 If you don’t have access to create service tokens, you can create a credential and contact your admin to create one for you.
If you don’t have access to create service tokens, you can create a credential and contact your admin to create one for you.- Team plans can create multiple service tokens that link to a single underlying credential, but each project can only have one credential.
- Enterprise plans can add multiple credentials and map those to service tokens for tailored access.
Book a free live demo to discover the full potential of dbt Cloud Enterprise.
3. View connection detail
-
Go back to the Project details page for connection details to connect to downstream tools.
-
Copy and share the environment ID, service token, host, as well as the service token name to the relevant teams for BI connection set up. If your tool uses the GraphQL API, save the GraphQL API host information instead of the JDBC URL.
For info on how to connect to other integrations, refer to Available integrations.
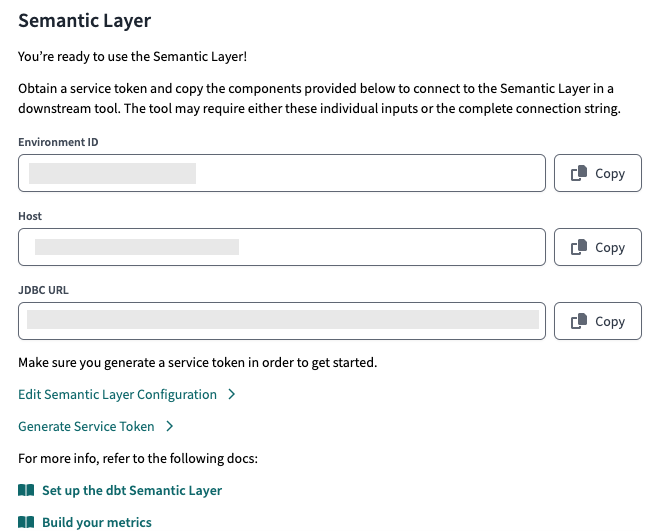 After configuring, you'll be provided with the connection details to connect to you downstream tools.
After configuring, you'll be provided with the connection details to connect to you downstream tools.4. Add more credentials enterprise
dbt Cloud Enterprise plans can optionally add multiple credentials and map them to service tokens, offering more granular control and tailored access for different teams, which can then be shared to relevant teams for BI connection setup. These credentials control the physical access to underlying data accessed by the Semantic Layer.
We recommend configuring credentials and service tokens to reflect your teams and their roles. For example, create tokens or credentials that align with your team's needs, such as providing access to finance-related schemas to the Finance team.
Note that:
- Admins can link multiple service tokens to a single credential within a project, but each service token can only be linked to one credential per project.
- When you send a request through the APIs, the service token of the linked credential will follow access policies of the underlying view and tables used to build your semantic layer requests.
-
Use Extended Attributes and Environment Variables when connecting to the Semantic Layer. If you set a value directly in the Semantic Layer Credentials, it will have a higher priority than Extended Attributes. When using environment variables, the default value for the environment will be used.
For example, set the warehouse by using
{{env_var('DBT_WAREHOUSE')}}in your Semantic Layer credentials.Similarly, if you set the account value using
{{env_var('DBT_ACCOUNT')}}in Extended Attributes, dbt will check both the Extended Attributes and the environment variable.
To add multiple credentials and map them to service tokens:
- After configuring your environment, on the Credentials & service tokens page, click the Add Semantic Layer credential button to create multiple credentials and map them to a service token.
- In the 1. Add credentials section, fill in the data platform's credential fields. We recommend using “read-only” credentials.
-
In the 2. Map new service token section, map a service token to the credential you configured in the previous step. dbt Cloud automatically selects the service token permission set you need (Semantic Layer Only and Metadata Only).
-
To add another service token during configuration, click Add Service Token.
-
You can link more service tokens to the same credential later on in the Semantic Layer Configuration Details page. To add another service token to an existing Semantic Layer configuration, click Add service token under the Linked service tokens section.
-
Click Save to link the service token to the credential. Remember to copy and save the service token securely, as it won't be viewable again after generation.
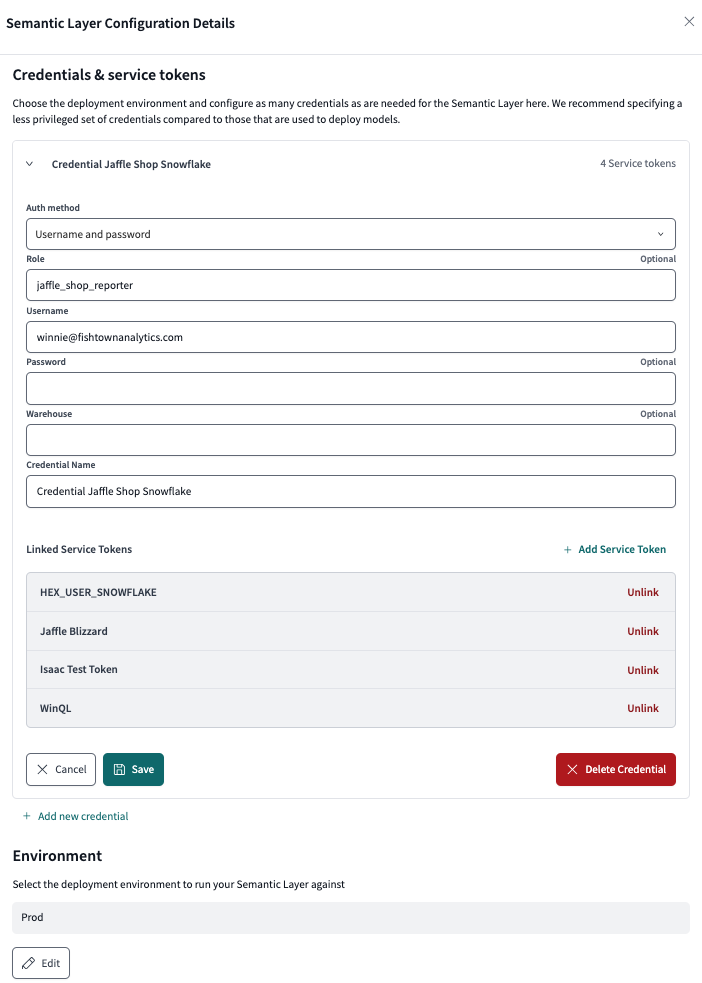 Use the configuration page to manage multiple credentials or link or unlink service tokens for more granular control.
Use the configuration page to manage multiple credentials or link or unlink service tokens for more granular control.-
To delete a credential, go back to the Credentials & service tokens page.
-
Under Linked Service Tokens, click Edit and, select Delete Credential to remove a credential.
When you delete a credential, any service tokens mapped to that credential in the project will no longer work and will break for any end users.
Delete configuration
You can delete the entire Semantic Layer configuration for a project. Note that deleting the Semantic Layer configuration will remove all credentials and unlink all service tokens to the project. It will also cause all queries to the Semantic Layer to fail.
Follow these steps to delete the Semantic Layer configuration for a project:
- Navigate to the Project details page.
- In the Semantic Layer section, select Delete Semantic Layer.
- Confirm the deletion by clicking Yes, delete semantic layer in the confirmation pop up.
To re-enable the dbt Semantic Layer setup in the future, you will need to recreate your setup configurations by following the previous steps. If your semantic models and metrics are still in your project, no changes are needed. If you've removed them, you'll need to set up the YAML configs again.
Additional configuration
The following are the additional flexible configurations for Semantic Layer credentials.
Unlink service tokens
- Unlink a service token from the credential by clicking Unlink under the Linked service tokens section. If you try to query the Semantic Layer with an unlinked credential, you'll experience an error in your BI tool because no valid token is mapped.
Manage from service token page
View credential from service token
- View your Semantic Layer credential directly by navigating to the API tokens and then Service tokens page.
- Select the service token to view the credential it's linked to. This is useful if you want to know which service tokens are mapped to credentials in your project.
Create a new service token
- From the Service tokens page, create a new service token and map it to the credential(s) (assuming the semantic layer permission exists). This is useful if you want to create a new service token and directly map it to a credential in your project.
- Make sure to select the correct permission set for the service token (Semantic Layer Only and Metadata Only).
Next steps
- Now that you've set up the dbt Semantic Layer, start querying your metrics with the available integrations.
- Optimize querying performance using declarative caching.
- Validate semantic nodes in CI to ensure code changes made to dbt models don't break these metrics.
- If you haven't already, learn how to build you metrics and semantic models in your development tool of choice.
- Learn about commonly asked dbt Semantic Layer FAQs.




